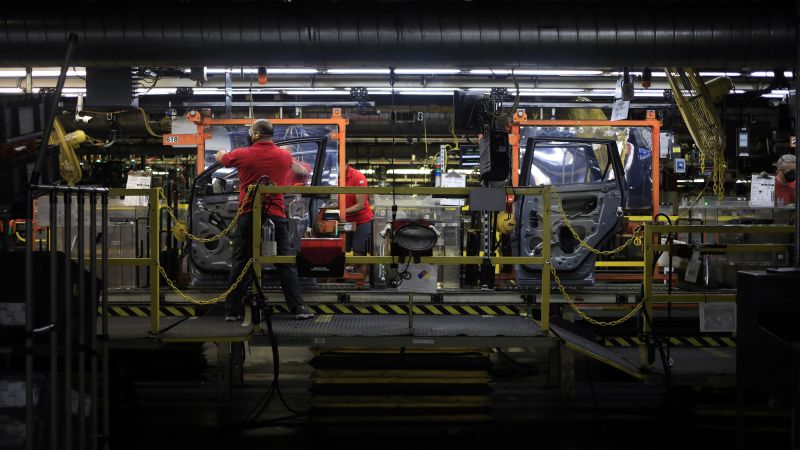
Looming over the United Auto Workers strike: Automakers’ continued migration to the anti-union South.
Beginning in the 1970s and 1980s, the auto industry began shifting South, a region long characterized by hostility to labor unions and by low wages.
Since then, assembly lines of higher-paid UAW workers at Detroit’s Big Three – Ford, General Motors and Stellantis – have shrunk. And automakers such as Volvo, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Toyota and Hyundai have steadily hired nonunion autoworkers, who make less money for substantially the same work, in the South.
The Big Three still depend on the UAW for work. Unlike some people claim, they don’t have the capacity, the time or the workforce to move production somewhere else. I doubt the UAW is all that worried.
Yeah, we’re about to be flooded with stories about how bad the UAW/ strike is for workers, business, the economy, and your Aunt Ethel. It’s all bullshit.
The really sad part is that they don’t even have to astroturf. They have an army of useful idiots who will post all kinds of anti-labor propaganda and not even realize it’s all a lie.
Those people exist because of the decades of anti union propaganda.
And wilful ignorance.
And unions doing foolish things that make them a bad option.
Thanks, but we did not need an example of someone who has fallen for the anti-union propaganda.
Why not? We have a number of examples here of someone who has fallen for pro-union propaganda.
Yeah workers organizing for mutual benefit and negotiation is totally dumb.
deleted by creator
…or those factories see what being unionized gets them and vote to unionize.
They should be worried because the big three haven’t adapted quickly enough.
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/usa-immigration-hyundai/
See guys? The non union workforce in the South is doing fine nothing to look at here.
One of these plants is right off an interstate and I drive past it frequently. Within a few weeks of this news breaking, there were “NOW HIRING” billboards put up for miles in either direction. Ignorance is a virtue in the American South.
deleted by creator
Removed by mod
Time to finish what Sherman started.
at least now it’s making a come back
Yeah, you guys do love your private prison slave labor, don’t you?
Hey stop making fun of them. You know their have the lowest rankings in education and quality of life. They won’t really understand it anyways.
Removed by mod
If they knew how to get things done why did they get their shit kicked in? So much for General Lee’s military genius and “know how to get things done.” SHERMAN AND DRUNK ASS GRANT DONE FUCKED YOU ALL UP.