Since I installed the official fan script, and it did nothing, I kept searching. I found a second user made script for controlling the fan, however I’m too inexperienced with linux to even understand what’s being asked.
Full page is listed at
https://gitlab.com/DarkElvenAngel/argononed
How To Install Firstly you need to have a build environment setup, that includes the following gcc dtc git bash linux-headers make git NOTE : The package names will be different depending on your OS so I’ve only given their binary names. Refer to your distribution for what you need to install. I’ve tried to make the installer as simple as possible. After cloning this repo simply run ./install You may need to reboot for full functionality.
What does he mean “build the environment setup”? And how do I clone a repo?
I’m trying this out on raspberry pi OS 64 bit, which is listed as compatible. If I can learn HOW to do this, I’ll do it on my main SD card OS, TwisterOS, which is also listed as compatible.
They are saying you need to know the distro package names on the command line. I don’t have a Rπ handy to check the packages for you. Use
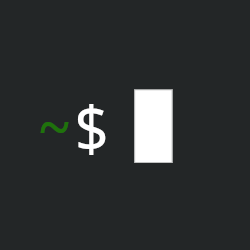
sudo apt-get install gcc dtc git bash linux-headers make gitthen see what fails. Whatever fails is likely just due to the package name being different in aptitude. The way you find the package name in Debian or any distro is a combination of searching different places and/or looking up the host repo on GitHub/GitLab/etc. Often they will list the names of the package in different distros.Note that, anything Debian based may be old and outdated in Aptitude packages. You can still use it just the same. It is old by design. That is what Stable distro means. If you find documentation online or you need some newer feature, you must install stuff manually. It is probably a non issue for you at this stage, but just be aware. If you see info about a ppa this is how you add the more recent packages to aptitude so that it overrides the older stable packages.
Ok, I did this in terminal.
bighat@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo apt-get install gcc dtc git bash linux-headers Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done Note, selecting 'raspberrypi-kernel-headers' instead of 'linux-headers' E: Unable to locate package dtc bighat@raspberrypi:~ $and then searched “raspberry pi os dtc package” and got this page
https://snapcraft.io/install/device-tree-compiler/raspbian
Is this what I want?
Firstly you need to have a build environment setup, that includes the following gcc dtc git bash linux-headers make git
You need to install those packages first. I’ve never used TwisterOS but looks like it’s related to Debian, so I guess you install stuff with
apt get stuff
To clone the repo click on the button “copy https clone url” at the top. Then on your system (where you want to clone it) type
git clone paste the copied url
You need to have all those packages installed in order to build the software. If your on the default pi OS,
apt installthem.Then you just run
./installto build it.If you have further issues, post the log errors.
have a build environment [set up]
Means that you need to have a C/C++ compiler and typical set of supporting tools installed so you can compile the program. For Debian (which Raspberry Pi OS is based on), the
build-essentialpackage will get you most of the way there - you can use the search tools at https://www.debian.org/distrib/packages to find which packages provide the other tools you needclone the repo
Means download the code using the
gittool - rungit clone <url>