I’m aware of what constitutes a decent password, but typing in 15-30 random characters each time I lock my computer screen is starting to get a bit taxing.
How secure does my user password really need to be and what are the threats to it? Does the same apply to a root-enabled user as a “regular” user when it comes to password security?
For context, my threat model doesn’t need to account for real people breaking in and accessing my computer, the damage would be very contained.
Bonus question - what are the risks of having a weak password on a root user on a spare laptop on the same network as my main device that is used exclusively for web browsing? Thanks.
Using random characters is dumb.
It incetivices you to write it down (which in and of itself isn’t a completely terrible idea).
As an IT guy, let me tell you, STOP using random passwords!
Use passphrases instead, it is far easier to remember a sentence than a random string of letters and numbers.
Battery horse staple
Correct!
I was twaching a class on how to use my company’s software, and I used this comic as an example for the class, and someone said “Hey, that’s the password we use!”
You can lead a horse to water, but you can’t make 'em battery staple.
Yeah that’s my preferred method too. Bitwarden’s password generator can create passphrases too, so I have it just create random ones for pretty much everything. The only ones I have to remember are the ones to unlock Bitwarden itself, and the one to unlock the decryption when I boot my PC up. So like two sentences essentially. I literally don’t even know what the passwords are to anything else lol.
Not to mention that if you want to type it in somewhere ( like your car for a Spotify account or whatever ) a passphrase like
Hunter7-Tower-Ballsy9is easier to type than some random gibberish with special chars.
Agreed - the message I was trying to convey is that I use a very secure password, which sacrifices convenience for security - is this necessary though? I have no concerns related to memorising or particular difficulties typing it out as it follows a passphrase structure for the most part.
If your password was “is this necessary though” it’s easy to remember and not difficult at all to type
If you are only relying on the password as security, then yes, if you use MFA in adition to a password, they also probably yes.
So yes.
Use a password manager instead.
Very inconvenient for a PC login. Also, you need a password you can remember for your password manager at least
Yeah, but you still need a password you can remember to unlock the password manager
Yes, but the problem is memorizing multiple passwords not one. The majority of ppl is able to memorize a single complicated password.
“nobody can crack this password in a million years” in pretty strong
Edit :
“nobody can crack this password in a million years with current technology”
That statement misses the advancement of technology
One can also mix in numbers and symbols and capital letters with their passphrase / sentence. Throw in a comma, exclamation mark, replace an l with 1, o with 0, etc. of course it’s diminishing returns with a sufficiently long passphrase but it can help against dictionary type attacks by adding additional mutations / steps to the cracking.
Years ago I worked at a company where they based server root/admin passwords on song lyrics. The person who came up with it clearly liked classic rock. I still remember at least one of them:
4ThoseAboutToRockWeSaluteYou!
Lyrics are a pretty good base. Especially in passphrase style with spaces if supported, along with punctuation and capitals/numbers. What sucks is when an account system can’t support a long password. That’s the most frustrating requirement for any service and the greatest vulnerability of all the common restrictions.
I just memorize 8 characters of gibberish. It is fast to type in.
I have also used a hybrid approach which is 2-3 words with ransom numbers and symbols
It is fairly easy to remember and not to hard to type in. I struggle with just a word list as I tend to misspell words or make typos. It also takes a while to type.
This is an interesting table for password cracking based on password hash…
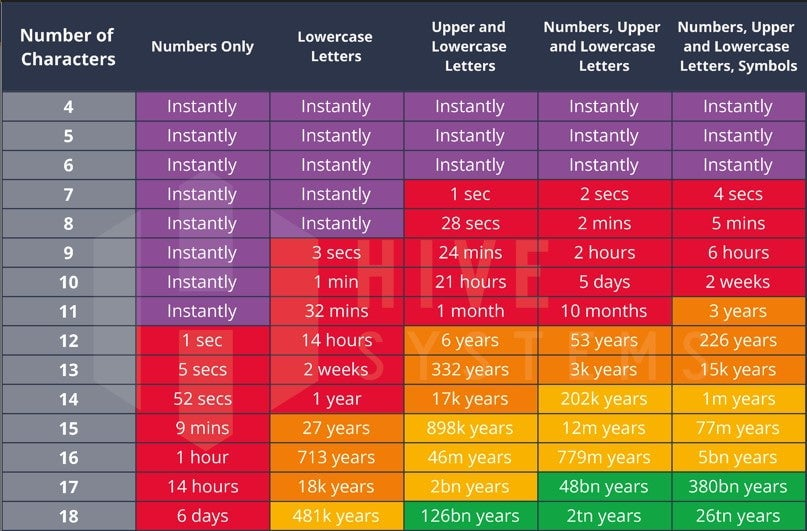
I was wondering why 1 year was in the red category, but then I realized that that time could decrease quite a bit over time with technological advances
EDIT: typo
The chart also doesn’t specify what hardware the calculation is based on. If it’s “1 year to crack for your average desktop PC”, then a server farm will do so in minutes.
The hash doesn’t matter from a device perspective. The OS enforces a retry delay and a person would need to use a keyboard.
This is for random characters but “interestingpassword” will get cracked by a dictionary attack almost instantly.
Lots of hand waving in this, but its good for relative comparison
Not a direct answer to your question, but you can use passphrases instead to make it easier and faster to type. This is assuming your only option to log on to your computer and unlock your screen is to type in your password (e.g. no biometrics or hardware token options).
No biometrics! Just wanted to clarify the only difficulties related to typing my password are its length
This is great advice! It’s the easiest way to create a long and difficult to crack password! Especially good for your laptop logon where you won’t have access to your password manager.
For context, my threat model doesn’t need to account for real people breaking in and accessing my computer, the damage would be very contained.
I mean if you don’t have open ssh ports on your computer or whatever I don’t think you need a strong password, given that you’re not concerned about physical access. I would say that at the very least have a reasonably secure root password (/user password if you’re a sudoer/anyone else who can get root permissions with your user account) because if you end up with some malware on your computer that can, say, enter passwords, you don’t want it to be ridiculously easy to bruteforce.
Great! This is the kind of answer I’ve been looking for. Thank you.
Not at all. If you think about security like if a thief was to steal your data then the only thing protecting you would be disk encryption. A password for login won’t prevent someone from taking your disk.
A password without disk encryption is useless. If you mean your super user password however this should be secure of course.
To address the “why”:
A user account, as defined by a username/password combination, can be used to access resources on the machine without logging in interactively on that machine. In a perfect world, you would only ever log in interactively on the machine using an account with restricted permissions, and when you needed to do “administraty” things, you would provide separate admin credentials at that time (sudo, runas, whatever your OS of choice supports).
Bonus question - what are the risks of having a weak password on a root user on a spare laptop on the same network as my main device that is used exclusively for web browsing?
If someone is able to compromise that root user on Machine A, then they may be able to leverage Machine A as a platform to attack any other devices on your network, or make Machine A into a zombie in their bot army to attack other targets anywhere, send spam, whatever malicious shenanigans they desire. (I know that’s pretty simplistic, there’s a whole lot of details left out, but that’s the gist of it.)
Also, nobody has yet mentioned the PIN option. I know that Windows machines (at least some of them, depending on configuration) allow you to configure a PIN for logon for local accounts. This PIN is only stored locally on the machine, and is not transmitted anywhere else. It’s basically a “shortcut” to the full password, and I think it can only be used for interactive logon.
Just like a chain, strength is determined by the weakest link
Use secure passphrase for ALL your devices on your network
To add on, create a separate network with WPA3 for your more sensitive devices and keep those IOT devices on their own network
I guess my question is why so? How vulnerable are my devices with a compromised device on the network?
If they get into a vulnerable device on your network and you have weak network security they can dictionary attack into the network. Or if you have UPNP enabled it’s already done. From there any device connected is compromised
Why? You can’t login remotely
Home computer? I wouldn’t even have a password. If someone has physical access to your PC there are ways for them to get what they want no matter how strong your password is. You just need it to be secure enough to prevent specific people you know have access from getting in. Family, friends, whatever. So basically the only risk is that you use a password that they know you use because you shared an account with them or something.
Physical security is more important than software security on laptops. In a public space it’s enough to have a shit password as long as there is one.
For ssh ports or remote desktop connections that don’t use pairing you definitely need a strong password. For local WIFI connections it’s not as important as your WIFI security though.
It doesn’t need to be crazy secure as there is a retry delay enforced by the OS.
If you are talking about LUKS2 then go with a passphrase
I use a pretty simple password in my PC and Laptop, since, in theory, I’m the only one with access to them (oh, and my wife, of course).
I just don’t have ssh enabled and the root passwords are ridiculously strong.